Linear vs. Non-Linear Learning: Understanding the Difference
Learning is a complex process, and it can take many forms. Two fundamental approaches to learning are linear learning and non-linear learning. These approaches differ in how they structure and deliver educational content, and both have their unique advantages and limitations. In this comparison, we'll explore the distinctions between linear and non-linear learning, and we'll also touch upon how adaptive learning fits into the picture.
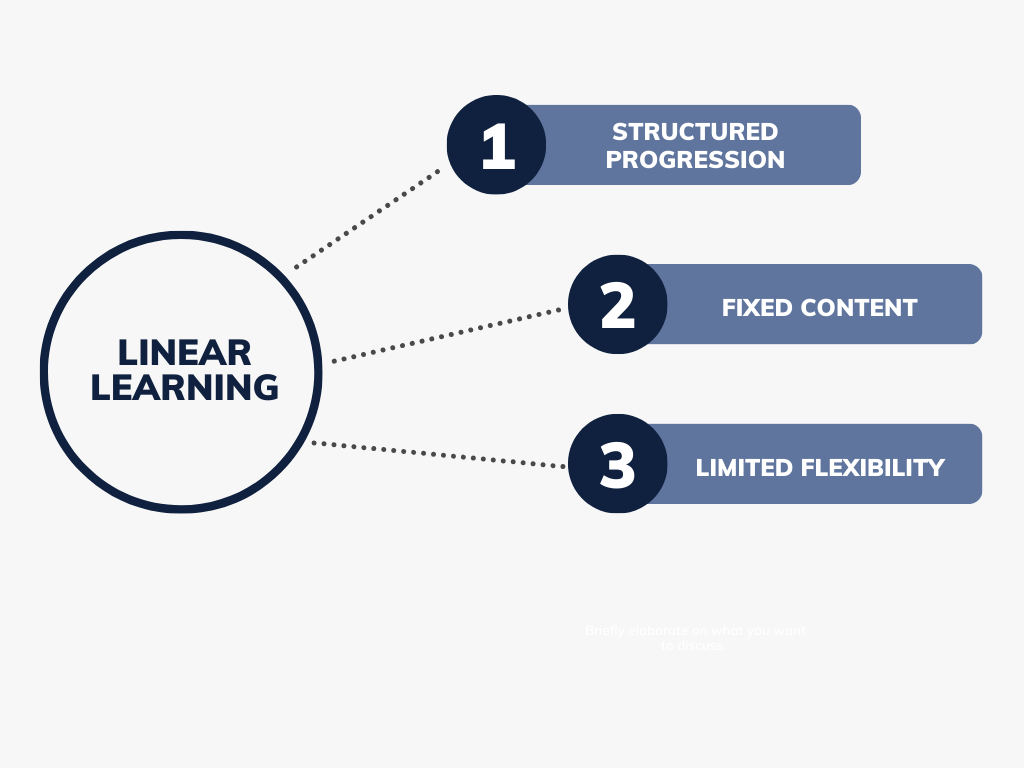
Linear Learning
Structured Progression: Linear learning follows a structured and predetermined path. Learners progress through the material in a predefined order, typically starting with basic concepts and gradually moving to more advanced topics. This approach is common in traditional classroom settings and many online courses.
Fixed Content: In linear learning, the content is fixed and uniform for all learners. Everyone goes through the same curriculum at the same pace. This can be efficient for ensuring that all students cover essential topics, but it may not accommodate diverse learning styles or individual needs effectively.
Limited Flexibility: Linear learning offers limited flexibility. Learners must adhere to the predefined schedule and content sequence, which may not cater to their unique strengths or weaknesses. This can lead to frustration for those who either struggle with the pace or find the material too easy.
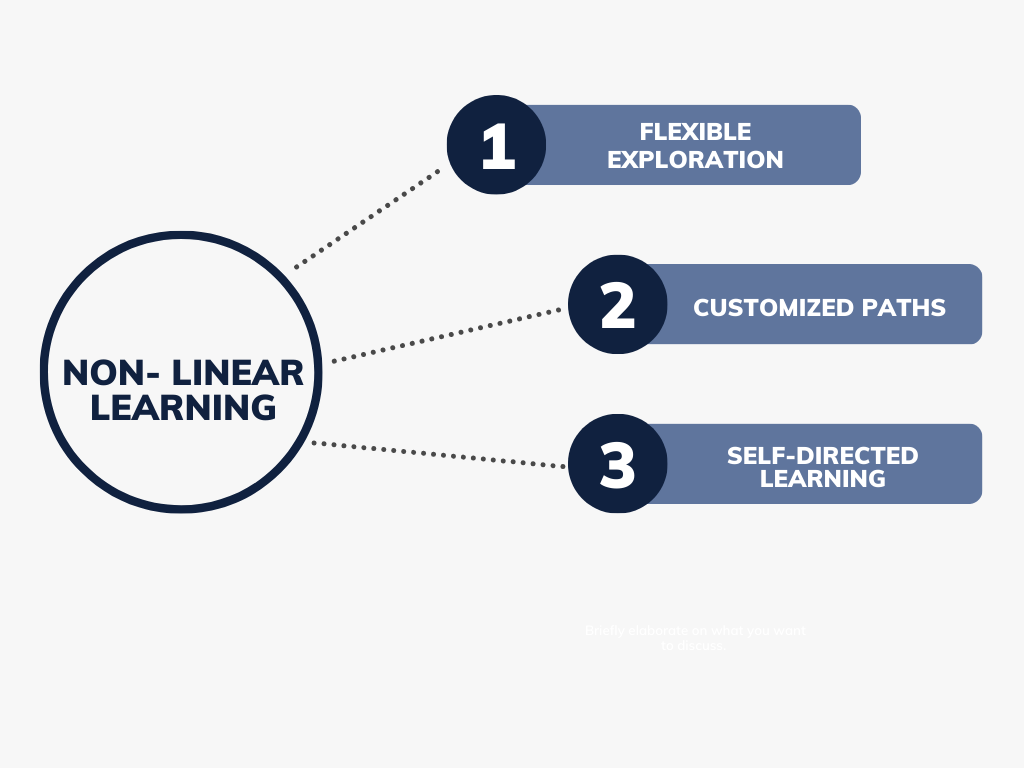
Non-Linear Learning
Flexible Exploration: Non-linear learning, on the other hand, allows learners to explore content more flexibly. Learners can choose the topics they want to study and in the order they prefer. This approach is common in self-directed learning, inquiry-based learning, and open educational resources.
Customized Paths: Non-linear learning often adapts to the learner's preferences and needs. It allows learners to skip over material they already know or dive deeper into areas they find particularly interesting. This customization can enhance engagement and motivation.
Challenges: Non-linear learning can pose challenges for individuals who require a structured learning environment or those who struggle with self-discipline. It may also lack a clear progression, making it difficult to ensure comprehensive coverage of a subject.
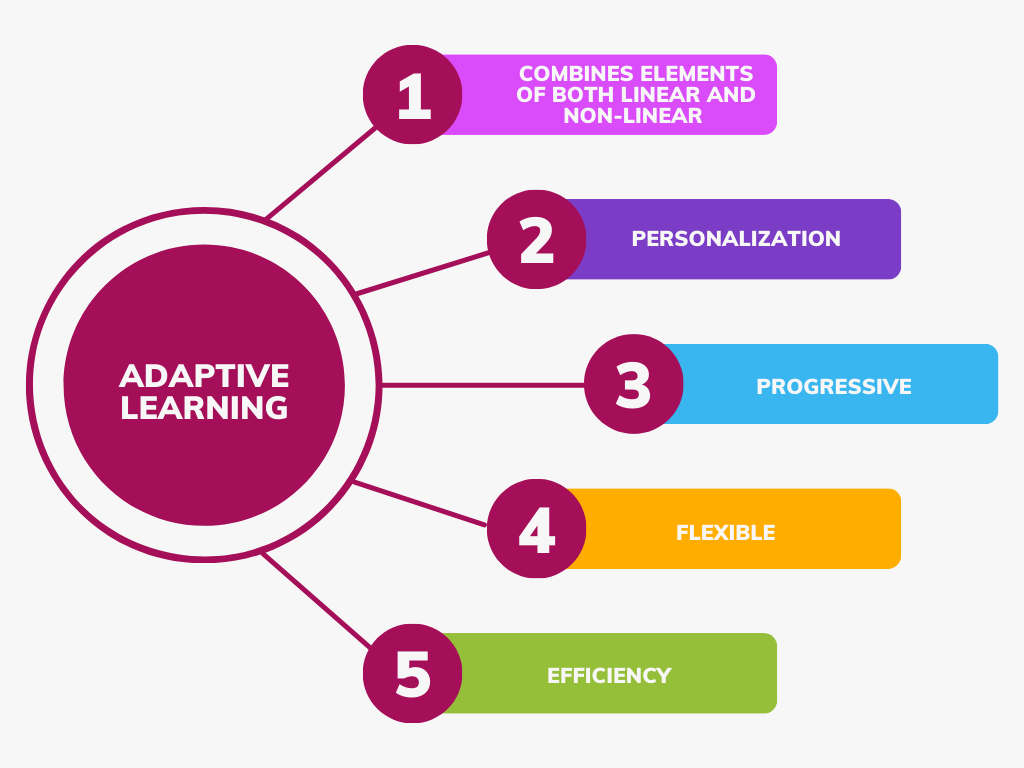
Adaptive Learning:
Adaptive learning combines elements of both linear and non-linear learning while incorporating advanced technology and data analysis. Here's how adaptive learning compares to these approaches:
Personalization: Adaptive learning systems use data-driven algorithms to assess a learner's strengths and weaknesses. Based on this assessment, they adapt the content, pacing, and difficulty level to the individual student. This personalization ensures that learners receive a tailored experience.
Progressive and Flexible: Adaptive learning systems provide a progressive path for learners while offering flexibility. They can adjust the learning sequence based on the learner's performance, ensuring that challenging concepts are revisited as needed.
Efficiency: Adaptive learning optimizes the learning process, making it more efficient by focusing on areas where the learner needs improvement. This can lead to faster mastery of topics and reduced time spent on material already well understood.
In conclusion, the choice between linear and non-linear learning depends on individual preferences, learning objectives, and the nature of the content being studied. Adaptive learning, however, bridges the gap by offering the benefits of both structured progression and flexible exploration. It leverages technology to provide a personalized and efficient learning experience, making it a powerful tool for modern education. Ultimately, the best approach to learning will depend on the learner's needs and goals.


